How to Choose the Right Roof Flashing for Optimal Protection and Performance
Roof flashing is a critical component in ensuring the longevity and functionality of a roof. As a barrier against water infiltration, it plays a vital role in protecting against leaks and damage. However, selecting the appropriate roof flashing requires careful consideration of various factors.
Understanding Roof Flashing
Roof flashing refers to thin pieces of impervious material, typically metal, installed in joints or valleys to direct water away from critical areas. It secures these points against water penetration, particularly where the roof meets chimneys, vents, and walls.
Importance of Choosing the Right Material
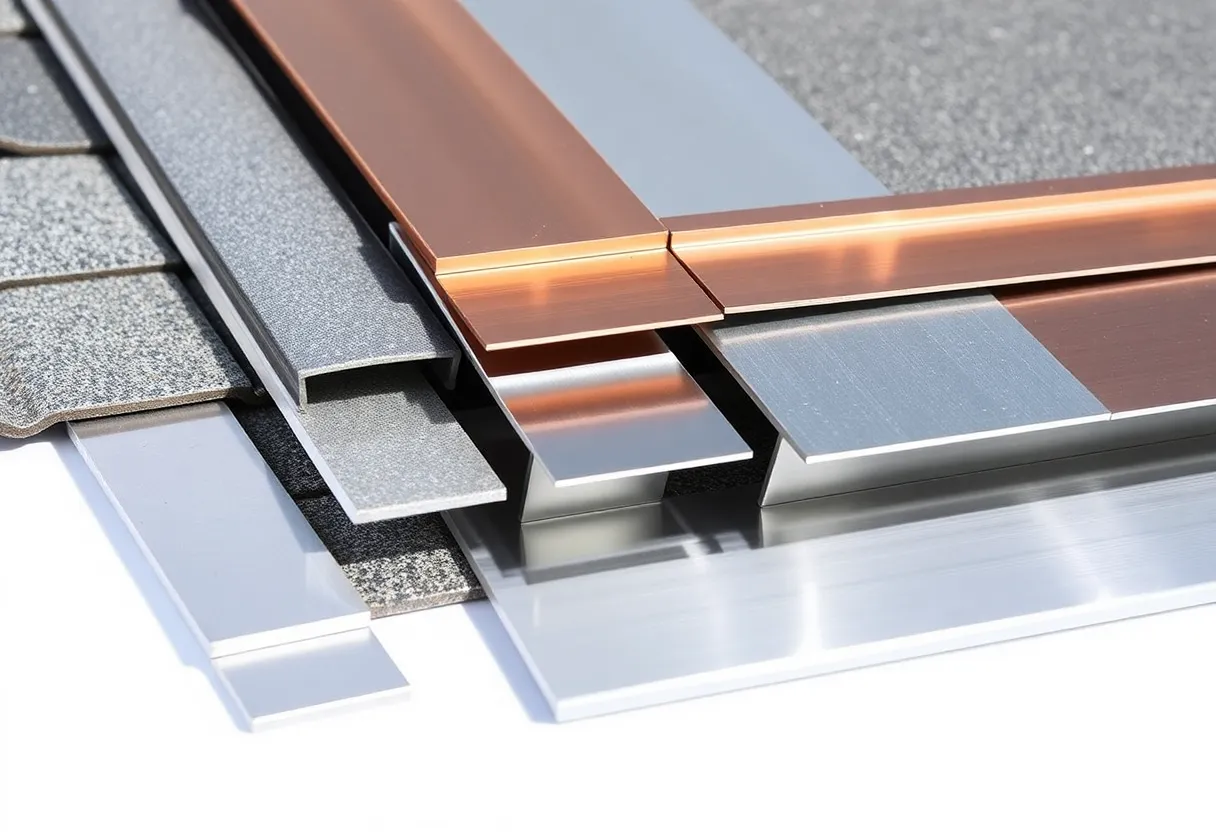
The material used for roof flashing significantly influences its performance, durability, and resistance. Below are some common materials for roof flashing:
1. Aluminum
Aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant. It is often used in residential applications due to its affordability and ease of installation. However, it may not be suitable for areas prone to extreme weather.
2. Copper
Copper flashing offers excellent durability and longevity. Its natural patina provides an attractive finish as it ages. Though initially more expensive, it can be cost-effective over time due to its lifespan.
3. Galvanized Steel
Galvanized steel is treated to resist rust, making it a popular choice for many roofing projects. It provides strong structural support but may be less resistant to corrosion compared to aluminum or copper.
4. Stainless Steel
Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and strength. It is ideal for areas exposed to harsh elements. The higher cost is often justified by its durability and effectiveness.
Assessing the Roofing System
The type of roofing system also influences the choice of flashing. Different roofs have unique profiles and pitches that affect water flow. Here are some considerations:
1. Sloped Roofs
For sloped roofs, having appropriately placed flashing is vital for directing water away from roof penetrations. Flashing should be installed along ridge lines and valleys.
2. Flat Roofs
Flat roofs require a different approach, often utilizing membrane flashing materials to create a waterproof barrier.
Understanding the design and construction of the roofing system will guide you in selecting appropriately sized and shaped flashing.
Compatibility with Roofing Material
Flashing material must be compatible with the roof covering. Using dissimilar metals can lead to galvanic corrosion. Here’s how to work with different roofing materials:
1. Asphalt Shingles
When working with asphalt shingles, install flashing made of aluminum or galvanized steel to prevent interactions that may lead to early degradation.
2. Tile Roofing
For tile roofing, copper flashing is recommended to complement the aesthetic and provide longevity. Care should also be taken to ensure compatibility with the tile material.
3. Slate Roofs
Slate roofs work best with copper or lead flashing solutions due to their durability and ability to withstand heavy elements.
Understanding Local Building Codes
Each region has building codes that dictate specific requirements for roof flashing materials and installation methods. Ensuring compliance is paramount—failure to do so may result in safety hazards and legal ramifications.
Environmental Considerations
Consider environmental factors that can affect roof flashing efficiency:
1. Climate
Areas with high rainfall, snow, or diverse weather patterns require durable, weather-resistant flashing materials to prevent leaks and structural damage.
2. UV Exposure
Flashing in areas exposed to high UV levels should be UV-resistant to maintain its integrity over time. Aluminum and galvanized steel are common choices for such environments.
Installation Techniques
The installation method is just as critical as the materials chosen. Proper installation enhances performance significantly. Here are several best practices:
1. Overlap and Seal
Ensure the flashing overlaps at least 1-2 inches at the seams and is properly sealed with roofing cement to prevent water from seeping underneath.
2. Slope the Flashing
The flashing should be sloped away from the roof penetrations to facilitate water flow instead of allowing it to pool.
3. Continuous Lengths
Use continuous lengths of flashing wherever possible to reduce seams and potential leak points.
Maintenance of Roof Flashing
Regular maintenance extends the life of roof flashing and ensures that it continues to perform its function effectively. Here are maintenance tips:
1. Inspect Regularly
Conduct inspections following extreme weather events to identify any damage, rust, or loose flashing.
2. Clean Debris
Remove debris and leaves that may accumulate around flashing to prevent water from pooling and creating backups.
3. Re-Seal Vulnerable Areas
Re-seal flashing periodically to maintain a watertight connection, especially in older roofs where sealant wears over time.
Conclusion
Choosing the right roof flashing is critical for protecting your roofing investment. Consider the material, compatibility with your roofing system, local building codes, and environmental conditions. Proper installation and regular maintenance will enhance performance and longevity. Making informed choices on flashing materials contributes greatly to the overall effectiveness and durability of your roof.
Invest the time in selecting the right flashing to guard against leaks and other problems that can compromise the integrity of your roof.




 Mays Contracting
Mays Contracting

